Save Your Energy!
A blog by Stanley Rayfield, Chartered Energy Manager
 As we move towards an all-electric lifestyle, how can we be sure that our efforts at home are making a difference? There are clearly some real drivers in reducing electricity consumption. Aside from the cost of the electricity itself, for many the emissions associated with burning fossil fuels in power stations is an important issue. So too is the desire to carefully conserve the pollution-free 50% of electricity generation that comes from renewables.
As we move towards an all-electric lifestyle, how can we be sure that our efforts at home are making a difference? There are clearly some real drivers in reducing electricity consumption. Aside from the cost of the electricity itself, for many the emissions associated with burning fossil fuels in power stations is an important issue. So too is the desire to carefully conserve the pollution-free 50% of electricity generation that comes from renewables.
So where do we start? Reducing energy waste is the first step. Energy efficiency has been described as the third fuel and luckily, some of the solutions are remarkably simple.
The power of off. The greenest energy is the energy that we don’t use. So often we focus on a technical solution to reduce consumption, but the simplest ways to reduce electricity consumption is to switch off things we aren’t using. Doing a sweep of your home electrical items is a good idea. Look for games consuls left on, TVs streaming from the internet and lights on in rooms where we are not, or seldom used items plugged in to endlessly charge. Switching off is a quick win, especially when we leave a room.
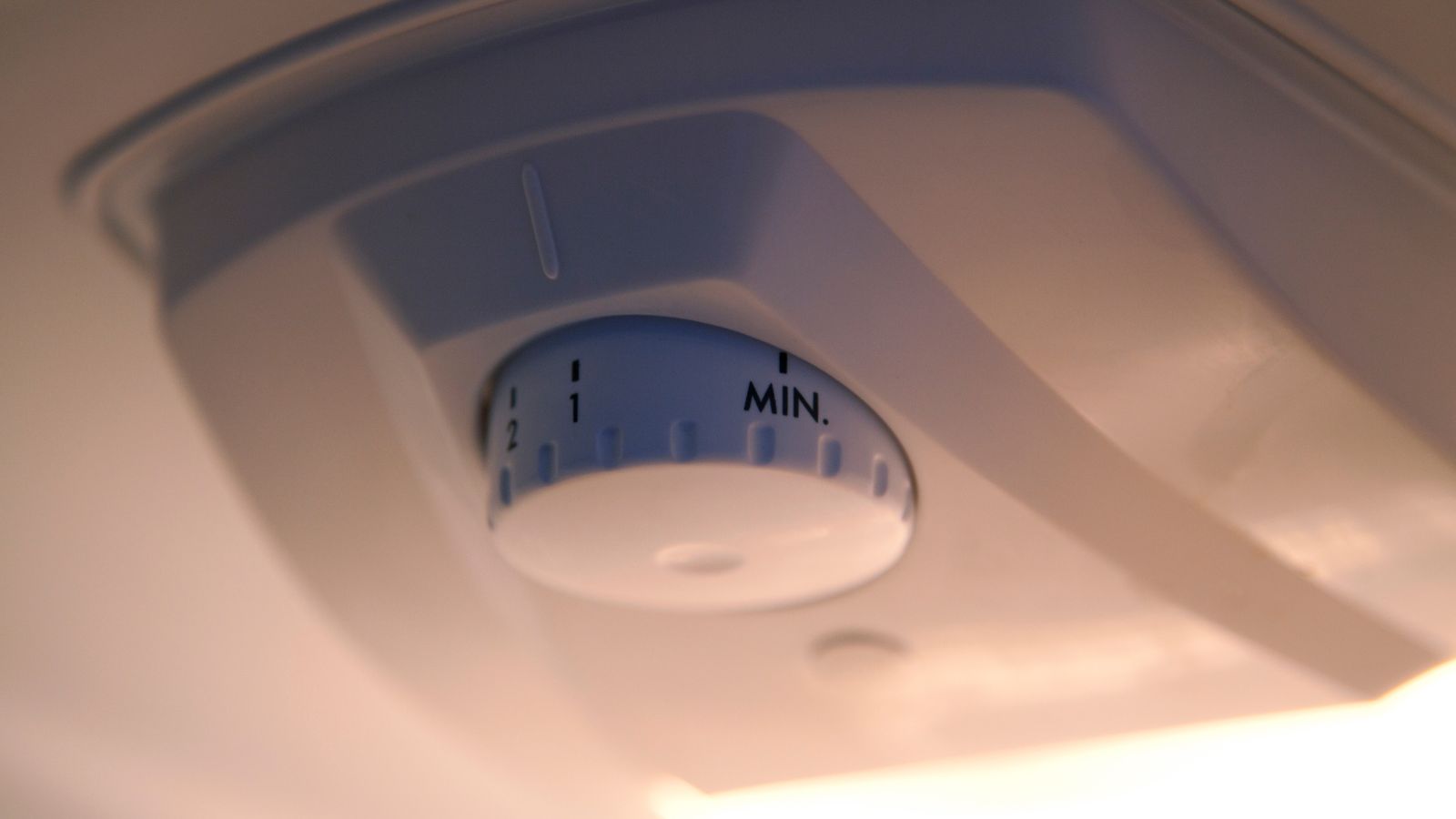

Green up your fridge. Having your fridge set at the right temperature makes a difference. Fridges operate for 365 days a year and small tweaks to the controls can keep the fridge set at the best practice temperature and limit the times that the fridge consumes too much electricity.
Such a simple task can be set back however, by the mystery of the dial inside the fridge. It’s often marked as high or low, max or min but few understand what that actually means. In fridges ‘higher settings’ means ‘lower temperature’. So the higher the dial is turned upwards, the colder the fridge will become. Taking time to set the recommended temperature (this tends to be around 4 degrees centigrade) will stabilise the electricity consumed.
Controlling your heating pump. Not many of us think about the electricity consumption from our gas boilers. Its common in summer to see a thermostat turned right down rather than having the heating system switched off altogether. The result is that the heating system’s pump often remains running all year around. Choose the ‘hot water only’ setting in summer to stop the central heating pump from consuming electricity.
Avoid swapping like for like. When an electrical item gets to the end of its serviceable life, find out its energy rating and purchase a more efficient replacement. Over time this has a real impact. Modern appliances are displayed with useful energy performance information that can be used for comparison. Electrical stores display the typical kWhs of energy per year for fridges and kWhs of energy and litres of water/per place setting for dishwashers. Modern appliances can be very efficient but there’s no guarantee the new item will automatically have lower consumption unless we research and select the best option.

Saving electricity not only helps reduce your energy bills, but also contributes to a greener environment. There’s not enough renewable energy to go around and even those on a genuinely renewable energy tariff can still make a difference to the pollution levels of our shared atmosphere. For every unit of renewable energy wasted, someone, somewhere will be consuming more electricity produced from burning fossil fuel.
To find out more about changing to a renewable tariff check out The Legal Renewables Initiative.
Stanley Rayfield is a Chartered Energy Manager with Achill Management and works with law firms to improve sustainability.
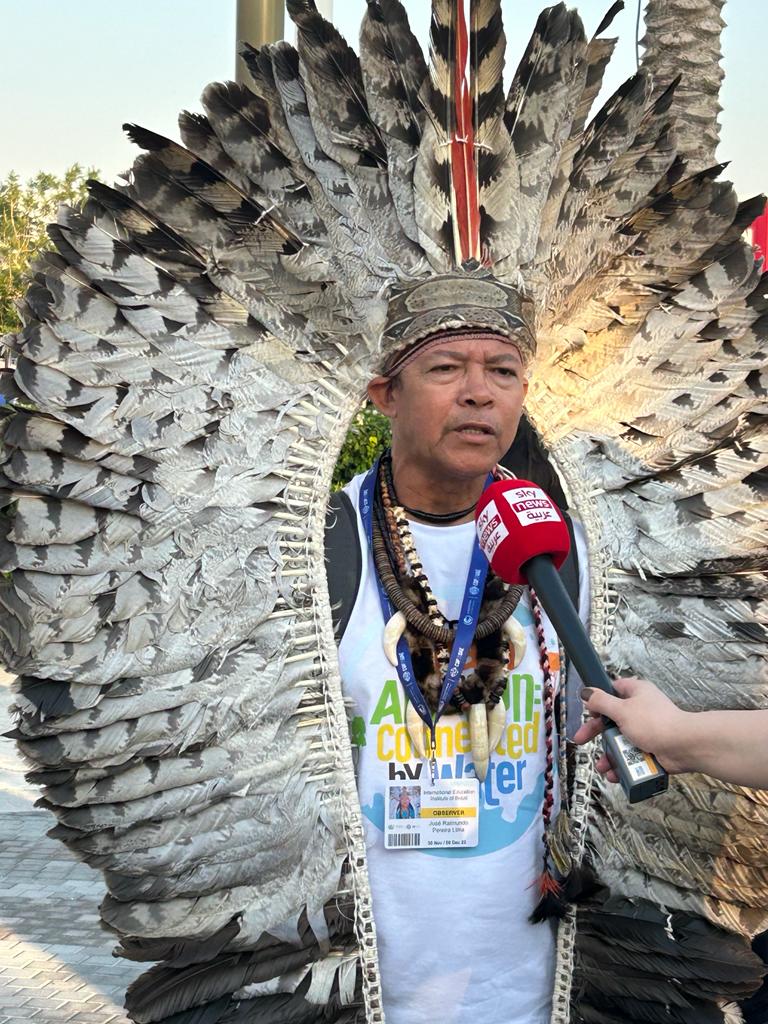









 COPs are amongst the most complex multilateral law and policy making processes in existence and LRI seeks to create a more level playing field by offering free legal advice and support to climate vulnerable and poorer nations during climate negotiations.
COPs are amongst the most complex multilateral law and policy making processes in existence and LRI seeks to create a more level playing field by offering free legal advice and support to climate vulnerable and poorer nations during climate negotiations. Working with a team of remote volunteer researchers, LRI also have capability to like help review and draft policy or review policy wordings, and when COP is not running, the organisation helps delegations and countries with capacity building.
Working with a team of remote volunteer researchers, LRI also have capability to like help review and draft policy or review policy wordings, and when COP is not running, the organisation helps delegations and countries with capacity building. Are you feeling hopeful after Day 1?
Are you feeling hopeful after Day 1?






 Reducing energy consumption reduces your carbon footprint, lowers operational costs and has a positive impact on the environment. Because the greenest energy is the energy that we don’t use, the LSA already works hard to support firms to reduce their scope 2 emissions through implementing energy efficiency measures and educating the workforce. However, we need to keep the lights on and offices warm – so when we do use energy, we want to ensure that it is the greenest energy available to us with the lowest environmental impact. That is where the Legal Renewables Initiative comes in.
Reducing energy consumption reduces your carbon footprint, lowers operational costs and has a positive impact on the environment. Because the greenest energy is the energy that we don’t use, the LSA already works hard to support firms to reduce their scope 2 emissions through implementing energy efficiency measures and educating the workforce. However, we need to keep the lights on and offices warm – so when we do use energy, we want to ensure that it is the greenest energy available to us with the lowest environmental impact. That is where the Legal Renewables Initiative comes in.