
by Beth Salt | May 6, 2025 | LSA Insights
World Environment Day 2025
In 2025, the focus of World Environment Day is on ending global plastic pollution. This year, it falls exactly two months before countries meet to continue negotiating a global treaty to end this pervasive problem.
Individual actions truly matter, but when we collaborate with colleagues to drive systemic change in our workplaces and across our supply chains, our impact is supercharged. By choosing to work with businesses that prioritise sustainability, we can help shift the entire sector towards smarter, plastic-free practices.
To mark World Environment Day we are urging LSA members to take the following pledge by downloading these graphics and sharing them on your social media channels, or by creating your own version using this copy.
Please tag us in your posts so we can amplify the message. Download images are high res, please feel free to co-brand and resize as appropriate.
The pledge:
We commit to tackling plastic pollution, by reducing our plastic footprint and supporting businesses who minimise theirs.
Find out more about World Environment Day here.
Graphics for Social Media:

by Beth Salt | Mar 31, 2025 | LSA Insights
Embedding Environmental Training in Law Firms – the Freshfields story
Law firms put environmental policies in place to help them measure and reduce their emissions – but why use valuable time and resources training staff about them?
We asked Mikey Bloxham, Environment Manager at Freshfields, which is directing its colleagues to undertake a mandatory education module on environmental topics.
Over 2025, the firm will roll out a global training module that is compulsory for all staff, partners and new joiners. This will be followed by a requirement to annually update knowledge.
“We understand the need to keep colleagues informed of work we are doing across the environment function for a number of reasons. Firstly, we want to help everyone understand why they are being asked to commit to practices that will reduce our emissions – for example, adopting to paperless working, adhering to the firm’s smart travel policy, turning their computer off at the end of the day, and correctly segregating any waste, amongst other things. We were also keen to keep colleagues up to speed with our climate action (offsetting) initiative and how we ensure that the project maintains integrity. Informed people are more likely to engage and take action. Lastly but also incredibly important, our lawyers now have these great talking points with clients.
“This is not only about existing employees, many of our new joiners, work experience students and scholarship candidates are asking us what we are doing in the environmental sustainability space. This is an important topic for people.”
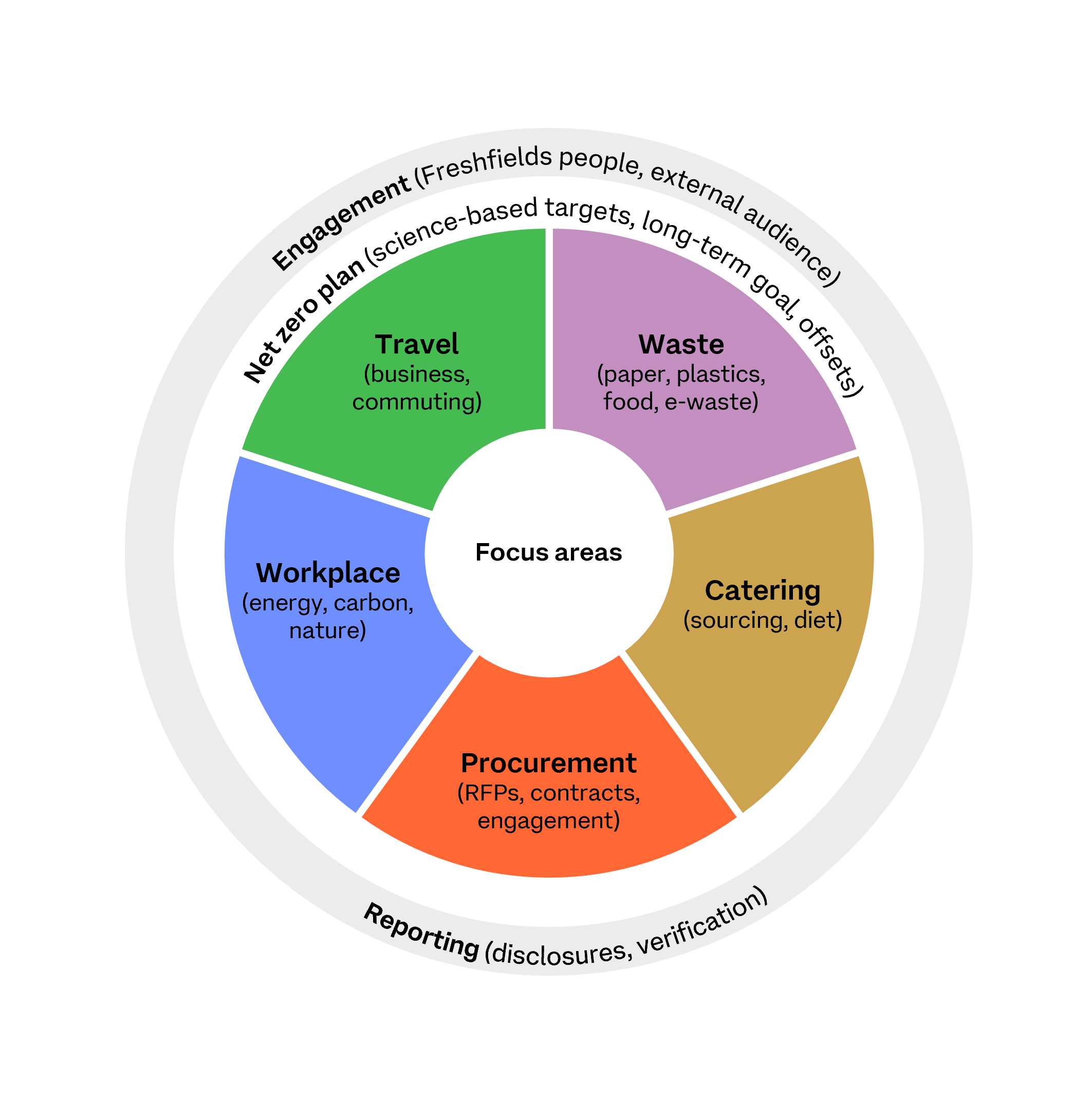
The firm has set itself a number of targets to achieve, including a 35% reduction in business travel-related emissions by 2027, and 100% renewable electricity supply to all offices by 2030, with these and other targets validated by SBTi. The environment team at Freshfields feel that education about the ‘why’ and ‘how’ of these targets will help galvanise employees and ensure their success.
Securing buy-in from senior leadership, including all regional COOs, has been crucial to the success of this upskilling, as was the need to create a standard module that functions internationally. This was a decision which inevitably presented challenges, with climate policies impacting regions in different ways. For instance, restrictions on business travel have a markedly different effect on Freshfields offices in Asia, compared to those in the UK. However, as collaboration is a cornerstone of effective climate action, Freshfields recognized the importance of adopting a unified, firmwide approach.
Education remains our most powerful tool, and engaging, empowering and informing colleagues and clients on how and why to take climate action will be a vital ingredient in the legal sector’s transition to net zero. If you are interested in finding out more about Freshfield’s training module then please get in touch here, the firm are happy to share the details of their experience in setting this initiative up. The LSA can organise an event/webinar to explore this area further if there is interest, please let us know.
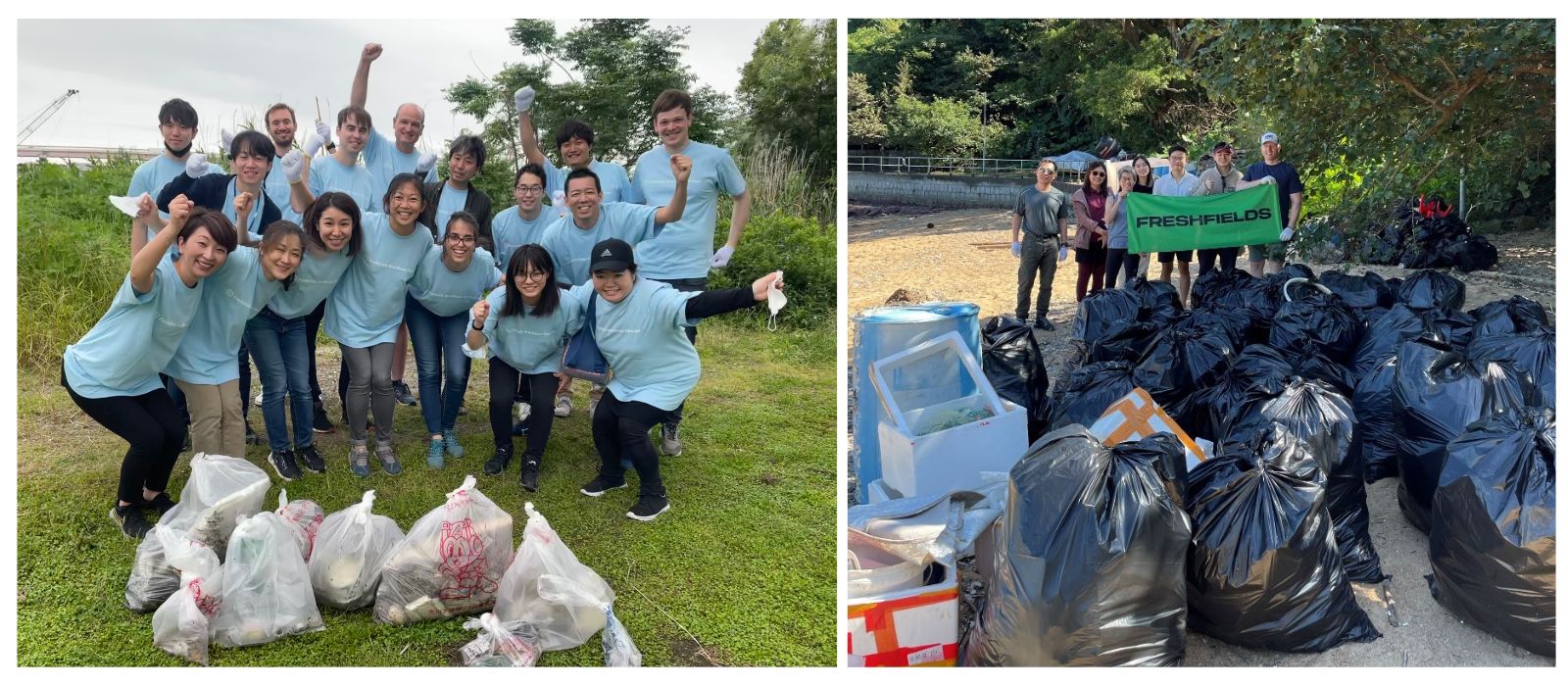

Freshfields teams perform a river clean up in Tokyo and a beach clean up in Hong Kong, steered by the global green group.

by Beth Salt | Feb 24, 2025 | LSA Insights
Empowering Action – How to start an environment and sustainability team in your law firm.
 By Lauren Spencer, Manager at Fragomen.
By Lauren Spencer, Manager at Fragomen.
Before diving into the steps for starting an Environment and Sustainability Team, or ‘green team’, it’s important to define what a green team is.
At Fragomen, our green team began in our UK office when a group of employees passionate about sustainability came together to explore ways to make our office more eco-friendly. That’s exactly what a green team is – a group of like-minded employees working towards a shared goal of creating a more sustainable workplace.
So, how can you start a green team in your organisation?
- Find interested team members
Start by gathering colleagues who share an interest in sustainability. Spread the word in a way that suits your workplace – send out an email, post on internal communication channels or even put up a poster (just remember to recycle it afterwards!).

If initial responses are low, you may need to take a more active approach. Speak with colleagues, bring it up in team meetings or ask managers to nominate a representative from their department. Having a diverse team with members from different areas of the company is key to making a greater impact.
Key departments to involve:
- Office Services and Facilities: They can drive change by choosing eco-friendly suppliers and improving energy efficiency
- Finance: Sustainability efforts often involve budget considerations, and having finance onboard can help secure funding for green initiatives
A well-rounded team ensures that sustainability becomes a company-wide initiative rather than a niche interest.
- Start Small
Once the team is in place, use your first meeting to brainstorm quick, achievable wins. What small changes require minimal cost and effort?
At Fragomen, our first steps involved reviewing office consumables and making eco-friendly swaps. We switched to eco-friendly toilet paper, eco-friendly cleaning supplies, ethical tea and coffee brands, recycled printer paper, and greener stationery suppliers. Once this conversation starts, you’ll find endless opportunities for improvement.

Starting with small, visible changes build momentum. When employees see the results-such as greener products in the office- it creates excitement and encourages wider engagement.
To maintain momentum, schedule regular meetings (monthly or bimonthly) and set a structured agenda. This keeps your team focused and ensures meaningful progress towards sustainability goals.
- Educate and Engage Employees
A green team’s impact grows when the wider workforce gets involved. The more employees connect with sustainability efforts, the more likely they are to adopt eco-friendly habits in their daily lives.
Interactive events and hands-on activities are among the best ways to engage colleagues.
At Fragomen, we hosted:
- Workshops on eco-friendly Christmas decorations: Teaching employees how to create sustainable Christmas decorations using recycled materials
- Clothes swap shops: Encouraging staff to refresh their wardrobe sustainably by swapping clothes instead of buying new ones
- Halloween costume swaps for colleagues’ children: Helping parents reduce waste and save money by exchanging pre-loved costumes
- Volunteering days – Giving employees opportunities to support community gardens and local woodlands
- Plants in the office: Bringing greenery into the office and promoting plant-based well-being
- Seasonal events: Consider running themed events or monthly challenges to keep employees engaged year-round. Whether it’s a ‘Plastic Free July’ challenge or a lunchtime sustainability talk, small efforts help foster an eco-friendly culture
- Engage Senior Leadership
Securing senior leadership involvement is crucial for a green team to gain traction. Leadership advocates ensure sustainability initiatives are taken seriously and integrated into broader company goals. Without top-down support, green teams often struggle to gain momentum, as great ideas risk being overlooked or deprioritised. Engaging leadership early helps teams drive meaningful change with the backing needed to turn ideas into action.
- Measure Success and Keep Growing
Track progress by setting measurable goals and celebrating achievements. Recognising success keeps motivation high and encourages long-term commitment from employees.

The Road to Green Teams
Starting a green team is a powerful way to make a difference in your workplace. With the right support, a clear vision and a team of passionate individuals, you can drive meaningful change and create a more sustainable work environment.
Fragomen is a global immigration firm with nearly 6,000 professionals and support staff across more than 60 offices worldwide.

by Beth Salt | Feb 5, 2025 | LSA Insights

The Launch of the LSA’s Nature and Biodiversity Working Group (by Jenni Ramos)
The Legal Sustainability Alliance has hosted several workshops on biodiversity and nature in recent years, with a particular focus on what it means for lawyers. Our 2024 summer event “A legal lifeline for nature” featured Clare Brook (CEO of Blue Marine) in discussion with Sharif Shivji KC (co-author of the legal opinion Nature-related risks and directors’ duties under the law of England and Wales).
Many assume that the intersection between law and nature is found primarily in litigation cases such as those pursued by Blue Marine Foundation, environmental law practice or planning law and biodiversity net gain regulations.
While these are important areas, the relevance of nature and biodiversity to many members of the LSA falls outside the sphere of environmental and planning law and emerges from the ‘business case for biodiversity’. The legal opinion described above found that nature-related risks and opportunities are highly relevant to the duties of company directors to act with care and promote the success of their company. This is due to the global recognition that biodiversity loss and ecosystem degradation pose financial risks to the entire economy and the companies and financial institutions within it. This places it firmly on the agenda of lawyers who advise companies across all practice areas. It is an emerging area of law that most lawyers are either unaware of, or only just beginning to grapple with.
Nature-related risks include physical and transition (including legal) risks. They can manifest in procurement and supply chain issues, strategic nature-related litigation (including cases relating to anti-money laundering, greenwashing and financial misrepresentation), insurance risk assessment and compliance with corporate and financial sustainability reporting and due diligence frameworks.
Nature-related risk is often viewed as a future concern or merely a compliance issue with incoming reporting regimes. Whilst the World Economic Forum’s Global Risks Report has in recent years consistently listed biodiversity as a top five risk over the next ten years, this framing of it being a future not immediate risk is misleading. The UK legal opinion (written by leading barristers primarily specialising in corporate and financial law) emphasised that a company’s nature-related dependencies or impacts had the potential to affect a company’s short term interests as well as its long term financial success. Nature related risks can be both acute and chronic in character and have the ability to manifest in cascading and compounding chains of events which could manifest rapidly in the short term.
The LSA is launching a Nature and Biodiversity Working Group to discuss how nature-related risks and their associated reporting regimes will affect member firms and clients. Members can explore issues they are facing, discuss where nature-related risks sit on their firm’s agenda and how it integrates with existing work on climate risk, sustainability reporting and supply chain due diligence. Members will lead the group’s direction, fostering knowledge sharing, identifying practical insights and potential outcomes.
As chair of the working group, I will be facilitating the first session, provisionally on 25th February at 12.30pm. Please email [email protected] if you would like to join us.
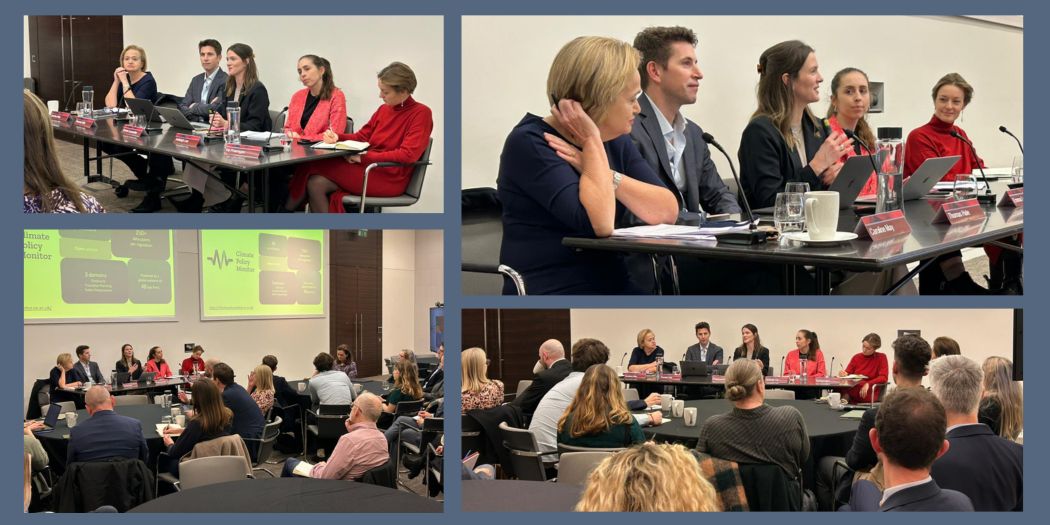

by Beth Salt | Jan 6, 2025 | LSA Insights
This LSA lunchtime event for exec firms was a great success, with nearly 50 LSA members enjoying the in-person session on transition planning. Huge thanks to our speakers for their valuable and interesting contribution. Thanks also to Caroline May of Norton Rose Fulbright for chairing the discussion and to Sarah Hickey and Paul Davies at Latham & Watkins for generously hosting the event. We asked our speakers for their key takeaways, listed below.

Speakers:
Thomas Hale and Emma Lecavalier, Blavatnik School of Government at the University of Oxford
Ashleigh Lee, City of London, UK Transition Finance Market Review
Ira Poensgen, LSE GRI, International Transition Plan Network
Takeaways:
Ira Poensgen, LSE GRI, International Transition Plan Network
– The Transition Plan Taskforce was set up in March 2022 with a mandate from the UK Government to bring together leaders from industry, academia, and regulators to develop good practice for transition plan disclosures.
– Key deliverables from the TPT include its Disclosure Framework, sector-specific guidance, a paper on legal considerations for transition plans, as well as technical mappings to various other standards and frameworks.
– As of June 2024, the IFRS Foundation has assumed responsibility for the TPT’s disclosure-specific materials. This transition represents a significant milestone in global efforts to harmonise transition plan disclosures.
– The TPT wrapped up in October 2024. In its final report, TPT recommended four areas for future efforts:
- Building market capabilities, practice and sharing experiences
- Developing enabling tools and driving thought leadership
- Ensuring that transition plans are integrated into decision-making: a) C-Suites and boards: Using transition plans as a change management tool. b) Investors and lenders: Enabling risk assessment, risk pricing, and informed capital allocation. c) Policymakers and regulatory authorities: Understanding transition trajectories and informing decision-making
- Increasing global consistency in transition planning norms and expectations.
– The team behind the TPT Secretariat has launched the new International Transition Plan Network to support the development of global norms for transition plans and planning.
Emma Lecavalier, Blavatnik School of Government at the University of Oxford
– Transition planning regulation is diverse: some regulation and policy targets corporate actors, but other rules use transition planning to coordinate across government or to shift sectoral performance (i.e. in energy, transportation, finance, agriculture).
– Transition planning is a valuable tool as governments look to organize economy-wide net zero transition. However, we need to be aware of risks that multiple rules can create friction or redundancy.
– Across all types of transition planning—corporate, national, and sectoral—we should be mindful of good practices such as: pairing disclosure with transition planning to enhance transparency and accountability; using third party verification and assurance to improve the data underpinning transition plans; and mainstreaming transition planning into spending (i.e. public and private procurement).
Ashleigh Lee, City of London, UK Transition Finance Market Review
– Companies and governments will require credible transition finance to deliver on decarbonisation commitments and meet Paris Agreement goals.
– The UK is uniquely positioned to become a leading hub for the transition finance market and use its leadership position for financial and professional services to accelerate the global transition. McKinsey & Company estimate that enabling the net-zero transition could bring in £1 trillion to UK businesses by 2030.
– The UK’s Transition Finance Market Review (TFMR) provides a framework to scale the market for transition finance in the UK and globally. Central to the findings of the Review are recommendations on how to unlock the required levels of finance by creating the right policies, pathways and signals for investment through collaboration between government, investors, business and civil society.
– Key recommendations of the Review include:
a) National sectoral transition planning and policy certainty: Scaling transition finance will require a greater level of granularity in sectoral transition pathways, greater collaboration with industry, and a greater level of coordination across government. The Review recommends a commitment to resourcing the Net Zero Council to deliver this granularity.
b) Catalytic capital and activity-level de-risking: Reaching commercial maturity for emerging transition activities will require effective policy, catalytic public capital, and public-private innovation. The Review recommends establishing a Transition Finance Lab to develop and test targeted financial solutions to tackle these challenges.
c) Transition planning and the supporting ecosystem: To move towards general-purpose transition finance predicated on a credible transition plan, the Review recommends mandatory Transition Plan Taskforce-aligned transition plan development and disclosure, and an evolution in the supporting data, assessment, verification, and assurance of transition plans.
d) Embedding credibility and integrity: The Review adopts a Transition Finance Classification System and proposes Guidelines for Credible Transition Finance. A principles-based approach to transition finance aids coalescence around core elements whilst enabling sufficient flexibility in other markets including emerging markets and for SMEs.
e) Delivering a roadmap for transition finance: Establish a Transition Finance Council to ensure delivery of the Review’s recommendations, as well as supporting capacity building, collaboration, and coordination.
For more information on any of the topics listed above, or to find out more please email the LSA manager Camilla on [email protected].

by Beth Salt | Jan 6, 2025 | LSA Insights
From collaborations to climate litigation, biodiversity to climate conscious pro bono – we asked our sustainability consultant colleagues to predict what trends might affect law firms committed to sustainability in 2025.
Sustainability trends affecting the sector:
- Sustainability Disclosure Standards (SDS): UK Sustainability Disclosure Standards are expected to impact businesses and potentially law firms themselves. Law firms will need to stay ahead of these to support clients and comply internally
- ESG reporting obligations: With enhanced ESG regulations, firms will need to guide clients on compliance with stricter supply chain rules, emissions disclosures and due diligence frameworks
- Advised Emissions: An emerging issue for law firms, linked to the growing risk of activist pressure on firms for their role in enabling high-carbon projects
- Increased spotlight on Carbon Markets: Voluntary carbon markets are here to stay, but expect greater transparency and a push to increase buyer confidence and market credibility
What might matter to your clients in 2025?
- Net-Zero mandates: UK law firms may develop a pathway and align with both client and the legal sector commitments to net-zero emissions, including operational carbon neutrality
- Sustainability regulations and compliance: Supporting clients as they comply with regulatory requirements including ISO, ESOS, SECR, TCFD and CSRD. Check out the LSA’s podcasts on these frameworks
- Biodiversity protection: Supporting businesses in compliance with biodiversity and ecosystem preservation regulations
- Climate adaptation policies: Advising clients on mitigating physical climate risks and risks to human health (e.g., extreme weather, resource scarcity, flood risk)
- Green finance: Advising clients on structuring green bonds, sustainability-linked loans and navigating ESG-related financing requirements
- Climate litigation: The rise of climate-related litigation opens new practice areas, both in prosecuting and defending cases tied to environmental impacts
- Rise in Greenwashing litigation: Lawyers will need to counsel clients on transparent ESG communications to mitigate the risk of such lawsuits
Sustainable operations within firms:
- Reducing carbon footprints: Matching client expectations that law firms are implementing sustainable practices within their own offices, such as energy-efficient and paperless workflows
- Sustainable procurement: Procurement that scrutinises the social, ethical and environmental products and services to achieve an overall level of best value
- Sustainable supply chains: Enlisting eco-friendly vendors and services for operations to support reducing scope 3 emissions in line net zero targets
- Pro bono climate action: Exploring opportunities to provide legal support for NGOs or climate initiatives working towards mitigating the climate crisis and ensuring climate justice
- SDGs: Embedding sustainable development goals with polices to support change
- Circular economy: Whereby the design and use of products are carefully planned to be adaptable for reused and repair
How law firms can position themselves as thought leaders in 2025?
- Walk the Walk: Strive for even more robust, transparent and comprehensive carbon reporting (especially scope 3) to avoid claims of greenwashing and demonstrate commitment to a transparency
- Green guide listings: Recognition in publications like The Legal 500 Green Guide for sustainability efforts could attract clients committed to ESG values
- Client collaboration: Partnering with like-minded clients on sustainability initiatives to build long-term, value-aligned relationships
- Hosting events and panels: Organising forums on sustainability topics to reinforce expertise and engage with the business community
- Communicating your sustainability successes: Use groups (like the LSA!) to amplify and share your sustainability stories on social media and in other comms. The LSA shares sustainability news via our website, our socials and our regular bulletin
How to communicate to colleagues why these trends are important?
- Attracting talent: ESG matters when recruiting. Offering meaningful sustainability policies will attract employees who value corporate responsibility
- Employee initiatives: Encouraging staff participation in green programs, like volunteering for climate action groups or leading internal sustainability initiatives, can improve wellbeing and support retention, as will robust and transparent policies designed to mitigate climate change










 By Lauren Spencer, Manager at Fragomen.
By Lauren Spencer, Manager at Fragomen.




